In today’s digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to cloud solutions to enhance their IT infrastructure. One such solution gaining prominence is the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). This technology offers a unique blend of security, flexibility, and control, making it an appealing choice for organizations seeking to optimize their cloud environments. This article explores what a VPC is, its key features, benefits, and how it can be leveraged effectively.
What is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
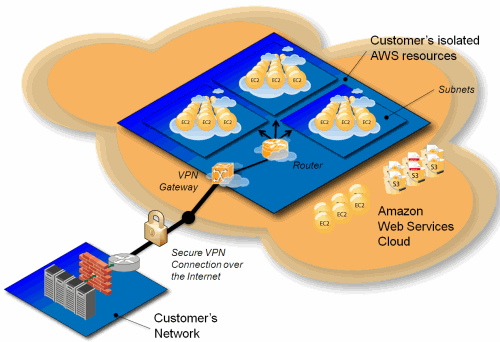
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a private, isolated section of a public cloud environment. It allows organizations to deploy and manage their resources in a logically isolated network that mimics a traditional on-premises data center. This virtualized environment is hosted within a public cloud infrastructure but provides enhanced security and control over the deployed resources.
The concept of a VPC enables users to have their own private network within a cloud provider’s infrastructure, with the ability to define and manage network configurations, such as IP address ranges, subnets, route tables, and network gateways. This isolation ensures that resources within the VPC are protected from other users of the same public cloud, offering a high level of data privacy and security.
Key Features of a VPC
One of the primary features of a VPC is its ability to provide a secure and customizable network environment. Users can set up private IP addresses, create subnets to segment their network, and configure network access controls to manage traffic between different parts of the VPC. Additionally, VPCs often support Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, which allow for secure communication between the VPC and on-premises networks.
Another important feature is the capability to use network address translation (NAT) to control outbound traffic. NAT gateways can be employed to allow resources within a VPC to access the internet while keeping the internal IP addresses hidden from the public domain. This adds an extra layer of security by ensuring that only necessary traffic is exposed to the outside world.
Benefits of Using a VPC
The benefits of implementing a VPC are manifold. One significant advantage is enhanced security. Since a VPC provides a logically isolated network, organizations can implement robust security policies and controls tailored to their specific needs. This isolation helps protect sensitive data and applications from potential threats and unauthorized access.
Flexibility is another key benefit of VPCs. Organizations can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, without the need for significant hardware investments. This elasticity allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing requirements and optimize their cloud expenditures.
Cost efficiency is also a notable advantage. By using a VPC, organizations can leverage the economies of scale provided by public cloud providers while maintaining a high level of control over their network environment. This combination helps reduce operational costs and improve overall financial efficiency.
Effective Utilization of a VPC
To make the most of a VPC, organizations should carefully plan their network architecture. This involves designing an effective subnet layout, configuring security groups and network access control lists (ACLs), and setting up appropriate routing rules. Proper planning ensures that the VPC is optimized for performance, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Another important consideration is the integration of a VPC with other cloud services. Many cloud providers offer a range of complementary services, such as load balancers, databases, and storage solutions, that can be seamlessly integrated with a VPC. Leveraging these services can enhance the overall functionality and efficiency of the cloud environment.
Regular monitoring and management are also crucial. Organizations should implement tools and practices to continuously monitor the performance and security of their VPC. This includes setting up alerts for unusual activities, reviewing access logs, and performing periodic security assessments.
Conclusion
The Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) represents a powerful and versatile cloud solution for organizations seeking a secure, flexible, and cost-effective IT infrastructure. By providing a private, isolated network environment within a public cloud, VPCs offer enhanced security, scalability, and operational efficiency. With careful planning and management, businesses can effectively leverage VPCs to optimize their cloud environments and meet their evolving needs.